First model forest in Ecuador

The Ibero-American Model Forest Network (Red Iberoamericana de Bosques Modelo) has made of the Andean Chocó (Chocó Andino) the first model forest in Ecuador.
Model forests are large scale forest areas that are sustainably managed. They include a variety of uses and land values, forms of management of resources and types of land management. The inhabitants are involved in the management in a participative manner.
The International Model Forest Network comprises, at the present time, more than 60 forests areas throughout the world. 30 of them are situated in various countries of Latin America.
The Andean Chocó
The Andean Chocó is a bio geographical region encompassing areas in Central America (in panama) and South America (in Colombia, Ecuador and Peru). It covers 187,400 km2, with humid tropical climate. Part of the Andean mountains are comprised in it, reaching 5,000 m asl in Ecuador. It is a biodiversity hotspot, with 9,000 species of vascular plants, 600 of birds and 200 of mammals, and a high endemic character (25% of plants and animals are endemic).
In Ecuador, the Commonwealth of the Andean Chocó (Mancomunidad del Chocó Andino) 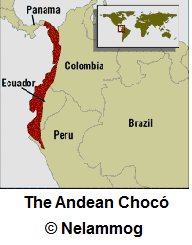 covers an area of 1,250 square kilometres, with about 18,000 inhabitants, in the Northwest of the Metropolitan District of Quito. The forest ranges from 500 to the 4,700 meters above sea level. 11 ecological systems, from the Moors to the rainforest piedmonts, can be individualized.
covers an area of 1,250 square kilometres, with about 18,000 inhabitants, in the Northwest of the Metropolitan District of Quito. The forest ranges from 500 to the 4,700 meters above sea level. 11 ecological systems, from the Moors to the rainforest piedmonts, can be individualized.
In the area, 320 archaeological sites are recorded. 60% of the territory is protected or sustainably managed, with three Areas of Conservation and Sustainable Use, a Heritage Reserve, part of the Natural Areas of the State, eight Protected Forests and 20 private and community reserves. The area is also part of the Ecological Corridor of the Andean Bear, one of the most endangered species in the region.
Future of the model forest
The management of the model forest is aimed at promoting sustainable uses in agriculture, animal husbandry, trade and tourism. It will comprise six strategic lines: conservation and restoration of natural heritage, land management, local governance and inter-agency management, sustainable production, information management and financial sustainability.
The main threat that the new model forest will have to face is constituted by the urbanization projects in the area.
(HT)